Week 8: Agile software development
by Andres Baravalle
Agile software development
- Software development phases
- Software development approaches
- Extreme Programming
Software development phases
Software development projects
In Web development, as in any other software development, projects can be divided into different phases - typically identified as:
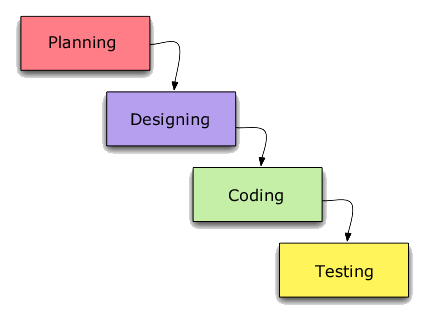
- Planning
- Designing
- Coding
- Testing
- Maintenance
Planning
During the planning phase the project requirements are collected (or extracted) from the relevant sources and formalised.
Interviews, focus groups and questionnaires can all be used to extract the software requirements.
Designing
In the designing phase, developers work at defining the structure of the system and the relations between the different sub-elements.
This includes formalising the requirements and modeling the application (Case Diagrams, User Stories etc).
Please note that designing (in this context) is about "application design" not "interface design".
Coding
Once the design is sufficiently clear, the team can proceed to the coding phase.
In this phase, we are going from the high-level description of the design phase, to actually doing the ‘manual’ work. In web applications development, it may require one or more of the following tasks: (X)HTML coding, client-side scripting, Web design or server-side programming.
Testing
The testing phase is used to analyse the result of the implementation in terms of correctness, completeness, security, and quality and to compare it to the initial requirements.
If a Web application is correct, complete, secure and of good quality but doesn’t fulfill the initial requirements, you may have a number of issues to discuss, either with your customer or with your project manager.
Maintenance
The maintenance phase is the final phase in a project, and follows the actual delivery of the project. The maintenance phase deals with issues that have been raised after the delivery: enhancing the software, optimising it and remedying its defects.
Software development approaches
Waterfall vs. Agile approaches
We have not yet said anything about how these phases are linked. Different approaches are possible, but the more common ones are known as the waterfall approach and the iterative (or agile) approach.
- Waterfall approaches emphasise a deep understanding of the system that is going to be developed and a strong attention to planning. Before ‘going down’ and implementing the system, the higher levels need to be sufficiently delineated.
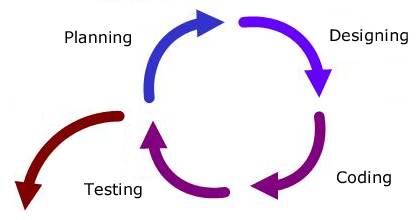
- Iterative (or agile) approaches imply an emphasis on starting the coding early and going through a progressive process in which additional components are planned, coded, designed and tested.
Waterfall approaches
Agile approaches
Agile approaches - cont'd
At first, the structure of the system is definitively at a high level, and then components are iteratively developed and refined. Iterations are typically short, with 1 to 4 weeks for a complete cycle.
This has the advantage of allowing testing at an early stage but may also imply that the structure of the system will be defined only in later stages.
In the following slides we will review two common agile software development methodologies: Extreme Programming and Scrum.
Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming (XP) is an agile software engineering methodology. Extreme Programming was developed in the early 1990s, by Kent Beck, Ward Cunningham and Ron Jeffries, as a way to escape from the disadvantages of the waterfall model.
XP advocates:
- Frequent "releases" in short development cycles
- Programming in pairs and, in general, extensive code review
- Face to face interaction among programmers
- Unit testing of all code
- Avoiding programming of features until they are actually needed
- A flat(ter) management structure
- Expecting non-fixated requirements
- Frequent contact with the customer
XP in practice
A set of twelve rules, grouped in four categories (fine scale feedback, continuous process, shared understanding, programmer welfare), are at the base of XP.Fine scale feedback
Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
Pair Programming |
Developers should work in couples, a driver (who types) and a navigator (who thinks). This typically leads to a better code, because there are two sets of eyes watching the code, while improving team cohesion and moral. The two developers should switch roles, at the very least once per day. |
Planning Game |
Includes release planning (initial and rough plan) and iteration planning (what to do next). There is no detailed, long-term plan in XP, and the planning game requires the involvement of the customer. |
Test Driven Development |
Define the tests before you start the implementation. |
Whole team |
Everyone responsible for the project should sit together regularly, including a representative for the customer. |
Implementing fine scale feedback
Rule |
Implementation in a Web project |
|---|---|
Pair Programming |
You need two persons working at the same computer at the same time. You shouldn't pair a Web designer with a Web developer, for example, unless they can work in both roles. |
Planning Game |
You can try a lighter version of the planning game by asking your customer to prioritise the stories that you develop. |
Test Driven Development |
Web application testing can be quite different from other types of testing. In most cases, the developers will have to define testing procedures (e.g. passing the W3C validation and passing a usability test). |
Whole team |
Involve the customer in all the phases, to make sure that he or she is comfortable with your choices. Instead of showing seven different designs to the customer, define it together. |
Continuous process
Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
Continuous Integration |
The developed components need to be continuously integrated. |
Design Improvement |
Improve step-by-step. You can improve the design after every iteration, when new components are integrated and built. |
Small Releases |
Release early, release often. |
Implementing continuous process
Rule |
Implementation in a Web project |
|---|---|
Continuous Integration |
Your web application should always be ready for demo. You shouldn’t have any non-included graphics, or orphaned pages waiting to be linked. |
Design Improvement |
The website is continuously refined when new components are available and integrated. |
Small Releases |
The website needs to be in a navigable form at the end of every iteration. |
Shared understanding
Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
Coding Standards |
Ensures that everyone can understand immediately the different parts of the project, and can immediately integrate new code. |
Collective Code Ownership |
Everybody is allowed to change everything in the project. |
Simple Design |
The design should be as simple as possible. |
System Metaphor |
Use an organising metaphor, a ‘shared story’ of how the system works. |
Implementing shared understanding
Rule |
Implementation in a Web project |
|---|---|
Coding Standards |
Use a consistent style for coding and design. If you write your JavaScript, HTML or PHP without spaces and tabulations (or inconsistent spaces and tabulations), it will be harder to modify for others. |
Collective Code Ownership |
Independently of the role in the project, everyone (Web developer, Web designer, project manager, etc.) can change anything in the implementation. |
Simple Design |
Don’t write unnecessarily complex code. Complexity is not given by length: allow more lines of code when it increases its understandability. |
System Metaphor |
Use a metaphor to describe your Web application. If it’s an e-commerce website, compare it to a shop. If it’s an online magazine, compare it to a newspaper. Find some metaphor for every project. |
Programmer welfare
Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
Sustainable Pace |
Programmers should not be over-stressed. |
This applies to every component of the development team. How do you do it?
What are the "stories"?
User stories are one or more short sentences in the everyday or business language of the end user of a system that capture what a user does or needs to do as part of his or her job function" (Wikipedia, 2013). User stories are used in agyle software development "as the basis for defining the functions a business system must provide, and to facilitate requirements management".
They are normally written using the formula:
As an X I would like to do Y so that I can Z.
Example:
“As a student, I would like to find my timetable so that I can attend my lessons”
Scrum
Scrum
Scrum is another agile software development methodology, focusing on continuous and incremental innovation.
As XP, it relies on self-organizing, cross-functional team with no leader.
In the next slides we are going to cover its main aspects and peculiarities: core roles, sprints, meetings and artifacts.
Roles
Scrum teams are based on three core roles:
- Product Owner: Represents the stakeholder and is the voice of the customer
- Development Team:Includes the persons responsible for delivering features as part of a incrementally developed project.
- Scrum Master: The Scrum Master enforces of the rules of Scrum, often chairs key meetings, and challenges the team to improve. It's not a Project Manager and does not have line management responsibilities.
Sprint
A sprint is an iteration with a fixed duration. Each sprint is preceded by a planning meeting and is the basic unit of development in Scrum.
Meetings
- Daily scrums: starts on time; standup meeting of max 15 minutes
- Scrum of scrums: daily cross-team meetings, to ensure co-ordination between different teams
- Sprint planning meeting: to select what will be done in a sprint; prepare the Sprint Backlog; identify how much work will be done in the sprint; eight-hour time limit
- Sprint review meeting and Sprint retrospective meeting: to review the work, present it to the customer (Sprint review) and reflect on the sprint just finished (Sprint retrospective)
Artifacts
- Product backlog: it's an ordered list of requirements, including business value (determined by the product owner) and estimated effort (determined by the development team). It's normally written in story format.
- Sprint backlog: it's the list of features to be implemented in a Sprint.
How do I implement this?
Most companies and developers typically don't follow any approach "word by word" but implement their own version - which can have elements of different approaches.Readings
Complement this week's lecture with further research and readings on the topics covered.
These are some pointers to start:
Pham, A.,
Pham, Phuong-Van (2012). Scrum in Action:
Agile Software
Project
Management and Development.
Wallace, D., Ragget, I. and Aufgang, J. (2002) Extreme Programming for the Web.
Wells, D. (2009). Extreme Programming:
A gentle introduction. Available from http://www.extremeprogramming.org/
Wikipedia (2013). Extreme Programming. Available from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extreme_programming
Wikipedia (2013). User story. Available from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_story
Wikipedia (2013). Scrum. Available from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrum_(software_development)
This work
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
